- Release Date:2025-09-09 08:00:11
- Reading volume: 0
Zhuanxiang Yi Finance and Taxation provides professional insights into the definition and levy targets of deed tax. Let Zhuanxiang Yi Finance and Taxation help you avoid those hidden pitfalls! We assist entrepreneurs in operating compliantly and mastering essential financial survival guides—saving money while staying compliant!
01 Definition of Deed Tax and Legal Basis
Deed tax refers to a type of tax paid to the state by the entity or individual that acquires the right to use land or ownership of a house during the transfer of such rights. Its main legal basis is the Law of the People's Republic of China on Deed Tax, which was adopted at the 21st Session of the Standing Committee of the 13th National People's Congress of the People's Republic of China on August 11, 2020, and came into force on September 1, 2021.
02 Object of Deed Tax Collection and Illustrative Examples
Deed tax is mainly levied on the transfer of the right to use land and ownership of houses, specifically including:
•Grant of the right to use state-owned land;
•Transfer of land use rights (including sale, donation, and exchange);
•Sale, donation, and exchange of houses.
Illustrative Examples:
•When an individual purchases a commercial residential property, they need to pay deed tax;
•When an enterprise acquires the right to use state-owned land through auction, it also needs to pay deed tax.
The taxpayers of deed tax are the entities or individuals that acquire the right to use land or ownership of houses.
03 Several Main Tax Rates of Deed Tax
According to the Law on Deed Tax, the general deed tax rate ranges from 3% to 5%. The specific applicable tax rate shall be proposed by the people's government of the province, autonomous region, or municipality directly under the Central Government within this range and submitted to the standing committee of the people's congress at the same level for decision. The following are examples of tax rates for common scenarios (taking Guangdong Province as an example):
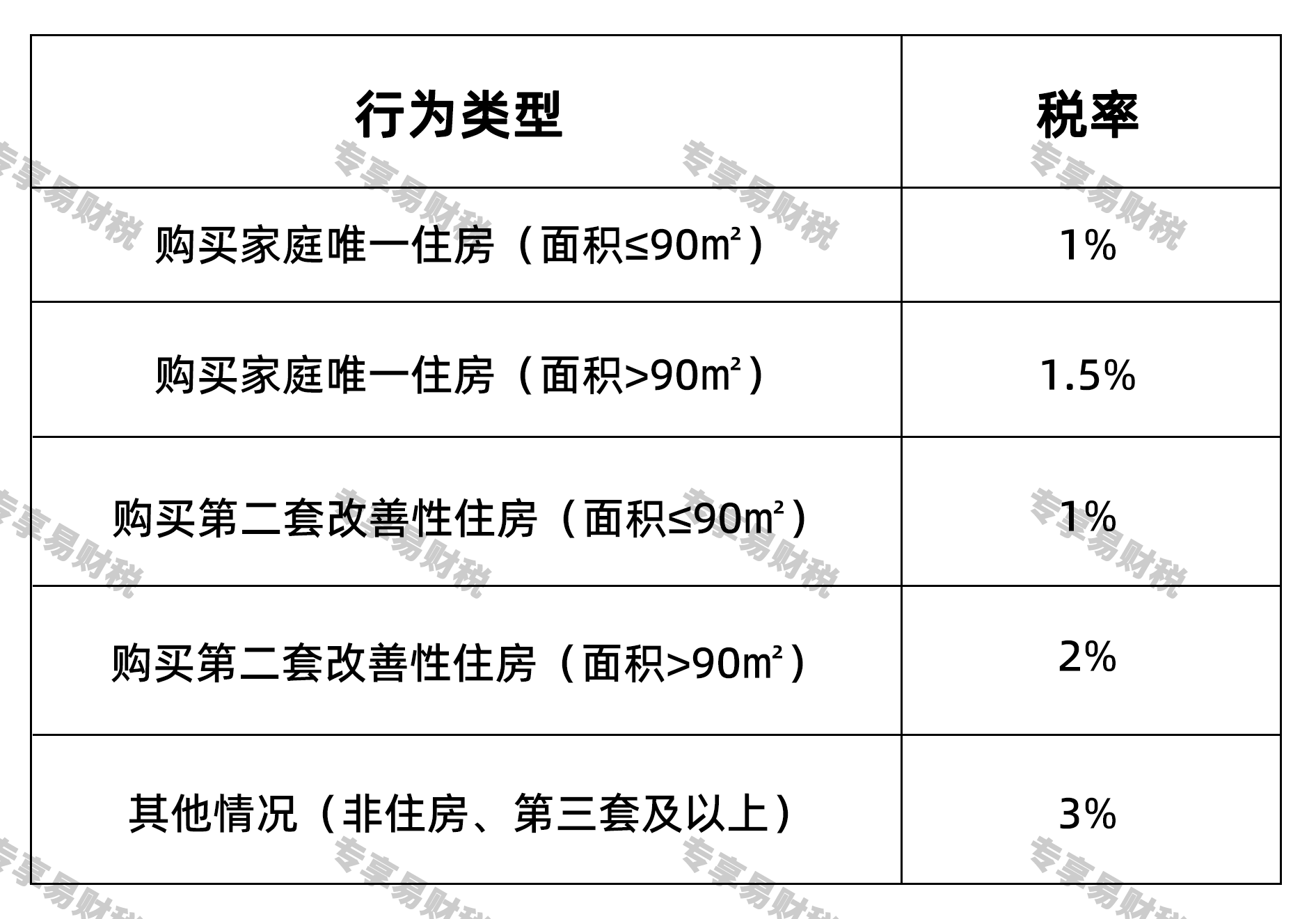
04 Preferential Policies for Deed Tax Reduction or Exemption
1. Main Scenarios for Deed Tax Reduction or Exemption
The preferential policies for deed tax reduction or exemption mainly include the following situations:
•State organs, public institutions, social organizations, and military units are exempt from deed tax when acquiring land or houses for office work, education, medical care, scientific research, or military facilities;
•Employees in cities and towns are exempt from deed tax when purchasing public housing for the first time in accordance with relevant regulations;
•If a housing property is lost due to force majeure and a new housing property is repurchased, deed tax may be reduced or exempted as appropriate;
•Other items for deed tax reduction or exemption as prescribed by the Ministry of Finance.
2 .Other Preferential Policies for Reduction or Exemption
(1)For financial leasing companies conducting sale-and-leaseback business, deed tax shall be levied in accordance with regulations when they acquire the ownership of the lessee's houses or land. When the sale-and-leaseback contract expires and the lessee repurchases the original ownership of the house or land, deed tax shall be exempted.
(2)When an entity or individual increases capital with assets other than houses or land, thereby increasing its proportion of equity holdings in the invested company, the ownership of the house or land does not transfer regardless of whether the invested company undergoes industrial and commercial registration changes, and thus no deed tax shall be levied.
(3)When the operator of an individual industrial and commercial household transfers the ownership of houses or land under their personal name to the individual industrial and commercial household, or when the individual industrial and commercial household transfers the ownership of houses or land under its name back to the original operator, deed tax shall be exempted.
(4)When a partner of a partnership enterprise transfers the ownership of houses or land under their name to the partnership enterprise, or when the partnership enterprise transfers the ownership of houses or land under its name back to the original partner, deed tax shall be exempted.
(5)Employees in cities and towns are exempt from deed tax when purchasing public housing for the first time in accordance with relevant regulations.
(6)Public rental housing management entities are exempt from deed tax when purchasing housing as public rental housing.
(7)Shantytown Renovation
Deed tax shall be exempted when the operation and management entity repurchases the allocated renovated resettlement housing and continues to use it as a source of renovated resettlement housing.
When an individual obtains monetary compensation due to house expropriation and uses it to purchase renovated resettlement housing, or conducts house property exchange due to house expropriation and obtains renovated resettlement housing, deed tax shall be reduced or exempted in accordance with relevant regulations.
(8)Deed tax shall be exempted for the poor population relocated from poverty-stricken areas when they obtain resettlement housing in accordance with relevant regulations.
(9)When a rural collective economic organization after the joint-stock cooperative system reform acquires the land or house ownership of the original collective economic organization, deed tax shall be exempted. When a rural collective economic organization, or a villagers' committee or villagers' group acting on behalf of the collective economic organization, reclaims collective assets through asset verification and acquires land or house ownership, deed tax shall be exempted.
(10)Deed tax shall be exempted for the operation and management entity of rural drinking water projects when it acquires land use rights for the construction of drinking water projects.
(11)Institutions providing elderly care, child care, and domestic services for the community are exempt from deed tax when they acquire houses or land for providing such community services.
(12)When a dissolved financial institution accepts the transfer of land use rights or house ownership from the debtor during the liquidation process to collect debts, deed tax shall be exempted for the transfer of such ownership.
(13)When China Orient Asset Management Co., Ltd. accepts real estate from Hong Kong-Macau International (Group) Co., Ltd. to offset debts, deed tax payable by China Orient Asset Management Co., Ltd. for acquiring house ownership and land use rights shall be exempted.
(14)From August 1, 2023 to December 31, 2027, deed tax shall be exempted for banking financial institutions and financial asset management companies when they accept debt-settling assets.
(15)From October 1, 2023 onwards, deed tax shall be exempted for the operation and management entities of indemnificatory housing when they repurchase indemnificatory housing and continue to use it as a source of indemnificatory housing. For individuals purchasing indemnificatory housing, deed tax shall be levied at a reduced rate of 1%.
05 Administration of Deed Tax Collection
Time of Occurrence of Tax Liability
The time when the tax liability arises is the date on which the taxpayer signs the contract for the transfer of land or house ownership, or the date on which the taxpayer obtains other certificates that have the nature of a contract for the transfer of land or house ownership.
•In case of transfer of land or house ownership due to effective legal documents issued by a people's court or an arbitration commission, or supervision documents issued by a supervision organ, the time of occurrence of tax liability shall be the date on which such legal documents or supervision documents take effect.
•If deed tax that has been reduced or exempted needs to be paid due to changes in the use of land or houses, the time of occurrence of tax liability shall be the date on which such changes in use occur.
•If supplementary land transfer fees need to be paid and deed tax is payable due to changes in land use conditions such as land nature and plot ratio, the time of occurrence of tax liability shall be the date on which such changes in land use conditions occur.
In the above-mentioned circumstances, if there is no need to go through the registration of land or house ownership in accordance with regulations, the taxpayer shall declare and pay deed tax within 90 days from the date on which the tax liability arises.
Tax Payment Period
Taxpayers shall declare and pay deed tax before going through the formalities for the registration of land or house ownership in accordance with the law. Taxpayers who meet the conditions for deed tax reduction or exemption shall declare in accordance with relevant regulations.
Place of Tax Payment
Deed tax shall be collected by the tax authorities at the place where the land or house is located.
Tax Declaration
When declaring deed tax in accordance with the law, taxpayers shall fill in the Detailed Statement of Tax Sources for Property and Behavior Taxes (the part of the Detailed Statement of Deed Tax Sources) and submit the following materials according to specific circumstances:
•Taxpayer's identity certificate;
•Contract for the transfer of land or house ownership or other certificates that have the nature of a contract for the transfer of land or house ownership;
•For the transfer of land or house ownership by means of delivering economic benefits, submit the payment certificate related to the transfer of land or house ownership. Among them, for the grant of land use rights, a fiscal bill shall be provided; for the sale or exchange of land use rights and the sale or exchange of houses, a value-added tax invoice shall be provided;
•In case of transfer of land or house ownership due to effective legal documents issued by a people's court or an arbitration commission, or supervision documents issued by a supervision organ, submit the effective legal documents or supervision documents.
For taxpayers who meet the conditions for tax reduction or exemption, they shall submit the relevant materials as required or keep the materials for future reference.
Deed Tax Refund
Before going through the registration of land or house ownership in accordance with the law, if the contract for the transfer of ownership or the certificate with the nature of a contract for the transfer of ownership becomes invalid, void, revoked, or terminated, the taxpayer may apply to the tax authority for a refund of the paid tax, and the tax authority shall handle the refund in accordance with the law.
Taxpayers may apply for a tax refund in accordance with relevant laws and regulations if the following circumstances occur after paying deed tax:
•Due to a judgment by a people's court or an award by an arbitration commission, the transfer of land or house ownership becomes invalid, revoked, or terminated, and the ownership of the land or house is changed back to the original owner;
•When the granted land use right is delivered, if the plot ratio is adjusted or the actual delivered area is smaller than the area agreed in the contract, resulting in the need to refund the land transfer fee;
•When a newly-built commercial housing is delivered, if the actual delivered area is smaller than the area agreed in the contract, resulting in the need to refund the housing price.
Other Administrative Provisions
•In case of transfer of land or house ownership due to effective legal documents issued by a people's court or an arbitration commission, if the taxpayer cannot obtain a real estate sales invoice, they may handle the deed tax declaration with the original copy of the people's court's execution ruling and relevant materials, and the tax authority shall accept the declaration.
•When a taxpayer who purchases a newly-built commercial housing handles the deed tax declaration, if the real estate development enterprise selling the newly-built commercial housing has gone through tax deregistration or been listed as an abnormal taxpayer by the tax authority, making it impossible for the taxpayer to obtain a real estate sales invoice, the tax authority shall accept the declaration after verifying the relevant situation.
06 Proportion of Deed Tax in China's Tax Revenue and Its Fiscal Status
Deed tax is an important part of China's local tax revenue. In recent years, it has accounted for approximately 3% to 4% of the country's total tax revenue. For example, in 2022, the national deed tax revenue reached several trillion yuan, providing a stable source of local fiscal revenue and playing an important role in ensuring local government public services and infrastructure construction.
07 Importance of Awareness of Tax Payment in Accordance with the Law
As a major tax category, the state has very strict policies on the collection of deed tax. Taxpayers should develop the awareness of respecting tax laws and paying taxes in accordance with the law, declare and pay deed tax in a timely manner, and avoid late fees or fines due to overdue payment or tax evasion, or even adverse impacts on personal or corporate credit. Paying taxes in accordance with the law is a legal obligation of every citizen and enterprise, and also a manifestation of social responsibility.

