- Release Date:2025-08-26 08:00:30
- Reading volume: 0
01 Definition of Individual Income Tax and Legal Basis
Individual Income Tax is a type of tax levied by the state on various taxable incomes obtained by natural persons (individuals). It is an important tax category that adjusts the interest distribution relationship between the state and individuals, and has the functions of raising fiscal revenue, regulating income distribution, and stabilizing the economy.
The main legal basis for China's Individual Income Tax is the Individual Income Tax Law of the People's Republic of China, which was reviewed and adopted at the 5th Session of the Standing Committee of the 13th National People's Congress on August 31, 2018, and came into effect on January 1, 2019. In addition, there are the Implementation Regulations of the Individual Income Tax Law of the People's Republic of China issued by the State Council, as well as a series of departmental rules and normative documents issued by the Ministry of Finance and the State Taxation Administration.
02 Taxable Objects and Scope of Individual Income Tax
Individual Income Tax is mainly levied on various taxable incomes obtained by individuals. According to the Individual Income Tax Law, taxable incomes include the following nine categories:
•Wages and salaries income;
•Remuneration for personal services income;
•Author's remuneration income;
•Royalties income;
•Business income;
•Interest, dividends, and bonuses income;
•Property rental income;
•Property transfer income;
•Contingent income.
Illustrative examples of situations requiring Individual Income Tax payment:
•An employee of a company receives a monthly salary of 8,000 yuan; the part exceeding the 5,000 yuan threshold needs to be subject to Individual Income Tax.
•A freelancer receives 15,000 yuan as remuneration for completing a design project and needs to pay Individual Income Tax based on remuneration for personal services income.
•A writer receives 30,000 yuan as author's remuneration for publishing a book and needs to pay Individual Income Tax based on author's remuneration income.
•An individual receives 4,000 yuan of monthly rental income from leasing their own house and needs to pay Individual Income Tax based on property rental income.
•An investor receives 10,000 yuan of dividend from a listed company and needs to pay Individual Income Tax based on interest, dividends, and bonuses income.
Taxpayers of Individual Income Tax include two categories: resident individuals and non-resident individuals. A resident individual refers to a person who has a domicile in China, or who has no domicile but has resided in China for a cumulative period of 183 days or more in a tax year, and is required to pay Individual Income Tax on their global income. A non-resident individual refers to a person who does not meet the conditions of a resident individual and only needs to pay Individual Income Tax on their income derived from sources within China.
03 Several Main Tax Rates of Individual Income Tax
China's Individual Income Tax adopts different tax rate forms according to different types of income:
1.Comprehensive income (wages and salaries, remuneration for personal services, author's remuneration, royalties) applies a seven-level progressive tax rate of 3% to 45%:

2.Business income applies a five-level progressive tax rate of 5% to 35%:

3.For interest, dividends, and bonuses income, property rental income, property transfer income, and contingent income, a proportional tax rate of 20% applies.
04 Preferential Policies for Individual Income Tax
China's Individual Income Tax Law stipulates a series of preferential policies, mainly including:
•Tax-exempt items: Including interest on national bonds and financial bonds issued by the state, subsidies and allowances issued in accordance with unified national regulations, welfare funds, pensions, relief funds, insurance indemnities, demobilization fees, resettlement fees, and retirement pay for military personnel, etc.
•Tax-reduction items: For income of disabled persons, the elderly without family support, and family members of martyrs, as well as cases where major losses are caused by severe natural disasters, Individual Income Tax may be reduced upon approval.
•Special additional deductions: Expenses incurred by taxpayers for children's education, continuing education, major medical treatment, housing loan interest or housing rent, and elderly support can be deducted in accordance with regulations when calculating the taxable income.
•Other tax preferences: For example, income obtained by individuals from transferring shares of listed companies is temporarily exempt from Individual Income Tax; for shares of listed companies obtained by individuals from public offerings and transfer markets, if the holding period exceeds 1 year, the dividend income is temporarily exempt from Individual Income Tax.
05 Standards and Details of Special Deductions for Individual Income Tax
Deduction items for Individual Income Tax include basic deduction expenses, special deductions, and special additional deductions:
1.Basic deduction expenses: 5,000 yuan per month (60,000 yuan per year), available to all taxpayers.
2.Special deductions: Include personal contributions to basic endowment insurance, basic medical insurance, unemployment insurance, and housing provident fund, which are deducted based on the actual amount incurred.
3.Standards and details of seven special additional deductions:
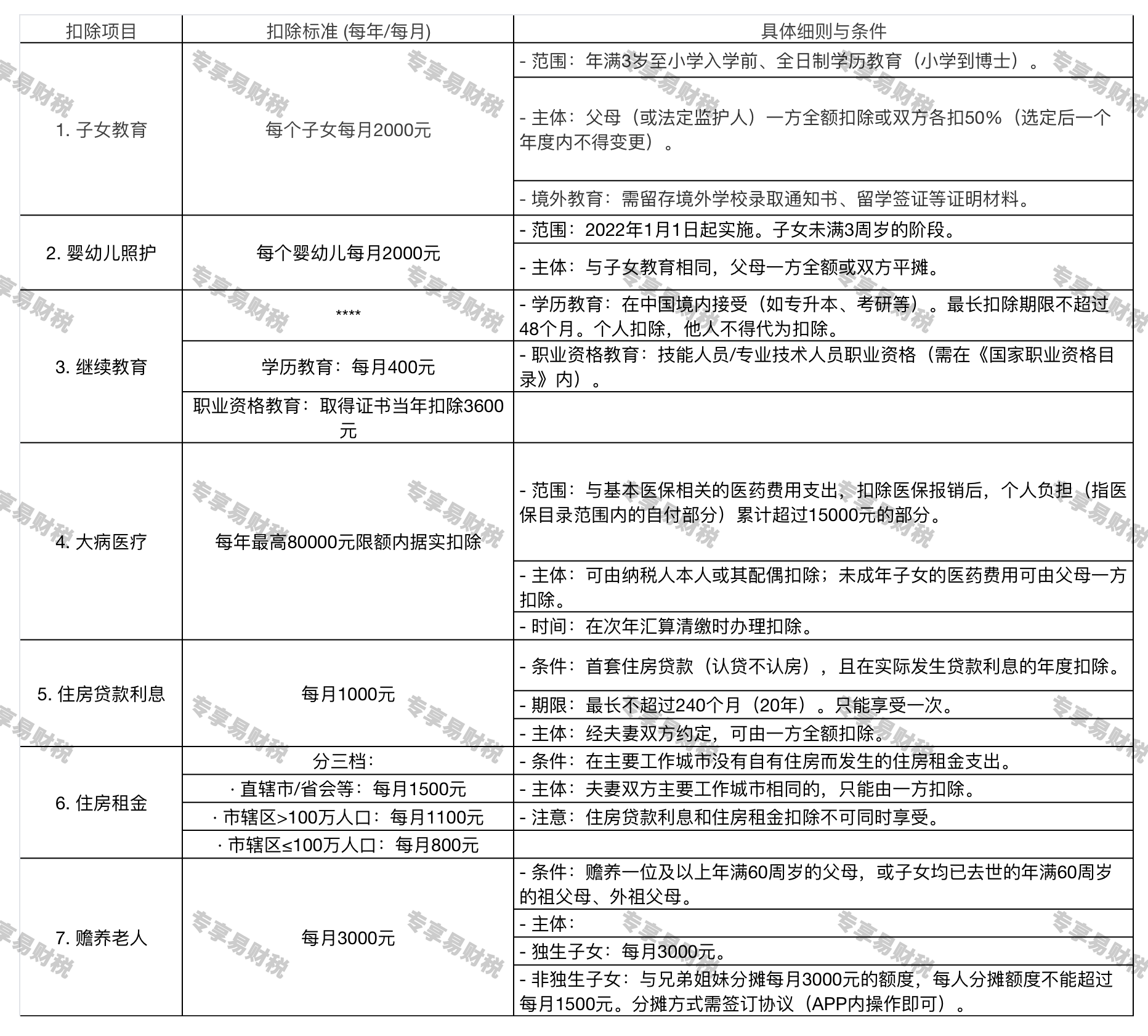
Note: The specific deduction standards and conditions may change with policy adjustments; please refer to the latest laws and regulations.
06 Proportion of Individual Income Tax in China's Total Tax Revenue and Its Important Status in China's Fiscal Revenue
Individual Income Tax is one of the important tax categories in China, and its proportion in China's tax revenue has been increasing in recent years. According to data released by the State Taxation Administration, the national Individual Income Tax revenue in 2022 reached 1.4923 trillion yuan, accounting for approximately 8.1% of the national total tax revenue (after deducting export tax rebates), and has become the fourth-largest tax category in China.
Individual Income Tax plays an important role in China's fiscal revenue:
•Raising fiscal revenue: It has become one of the important sources of fiscal revenue for local governments.
•Regulating income distribution: Through measures such as progressive tax rates and special additional deductions, it adjusts the income of high-income groups, reduces the tax burden on middle- and low-income groups, and promotes social equity.
•Economic stabilization function: It has an "automatic stabilizer" function—tax revenue increases to curb overheating during economic prosperity, and tax revenue decreases to stimulate the economy during economic recession.
•Reflecting economic development: The growth of Individual Income Tax is closely related to the growth of residents' income and the level of economic development, and it is an important indicator to measure economic development and residents' living standards.
07 Awareness of Respecting Tax Laws and Paying Taxes in Accordance with the Law
As one of China's major tax categories, the state has very strict collection policies for Individual Income Tax. Paying taxes in accordance with the law is an obligation of every citizen and an important symbol of social civilization and progress. We should:
•Enhance tax payment awareness, consciously fulfill tax obligations, and pay Individual Income Tax on time and in full.
•Earnestly study tax laws and regulations, understand our rights and obligations, and correctly calculate and declare Individual Income Tax.
•Properly keep vouchers and materials related to tax payment, and cooperate with tax authorities in inspections and verifications.
•Enjoy tax preferential policies through legal channels, and refrain from false declarations or tax evasion by means of deception or concealment.
•Actively understand changes in national tax policies and adjust personal tax planning in a timely manner.
Paying taxes in accordance with the law and in good faith is not only conducive to the stable growth of national fiscal revenue but also helps individuals accumulate a good tax credit record, which is of great significance in a modern credit society. For acts of deliberately evading tax obligations, tax authorities will pursue the payment of taxes in accordance with the law, impose late fees and fines; if the act constitutes a crime, criminal responsibility will also be pursued in accordance with the law.

